How to Create VTube CSV Reports (Including CSV Report Automation)
CSV reports are available as of version 4.4 build 1815, April 21, 2025.
Custom Report Template Design - Did you know that our SMA service includes custom-design report templates if requested? If you need a report template and your VTube SMA is active, contact support@advancedtubular.com for help.
What CSV Reports Are and How They Work
- A CSV report is a text file filled with comma-separated values that can easily be imported into systems outside VTube.
- The final reports don't contain HTML formatting tags because they are intended to be less complex than HTML-formatted reports, so external processes can read them more easily.
- They are editor-friendly. They can be viewed and read in any editor like Notepad++.
- Instead of creating an HTML report template, you will create a report template you know will be used as a CSV template.
- It will not contain all the HTML tags that are in formatted reports.
- Like HTML report templates, the same VTube variables are available for CSV report templates. Any value or array of values in VTube can be output in any CSV report or file in any order based in a customer-designed CSV format.
A Quick Overview of Both HTML and CSV Formats
Example Report Templates Designed for CSV Formatting
Each report template should be designed with either HTML or CSV format reports, but not both, because the internal formatting is different. For example, CSV templates don't contain HTML formatting tags.
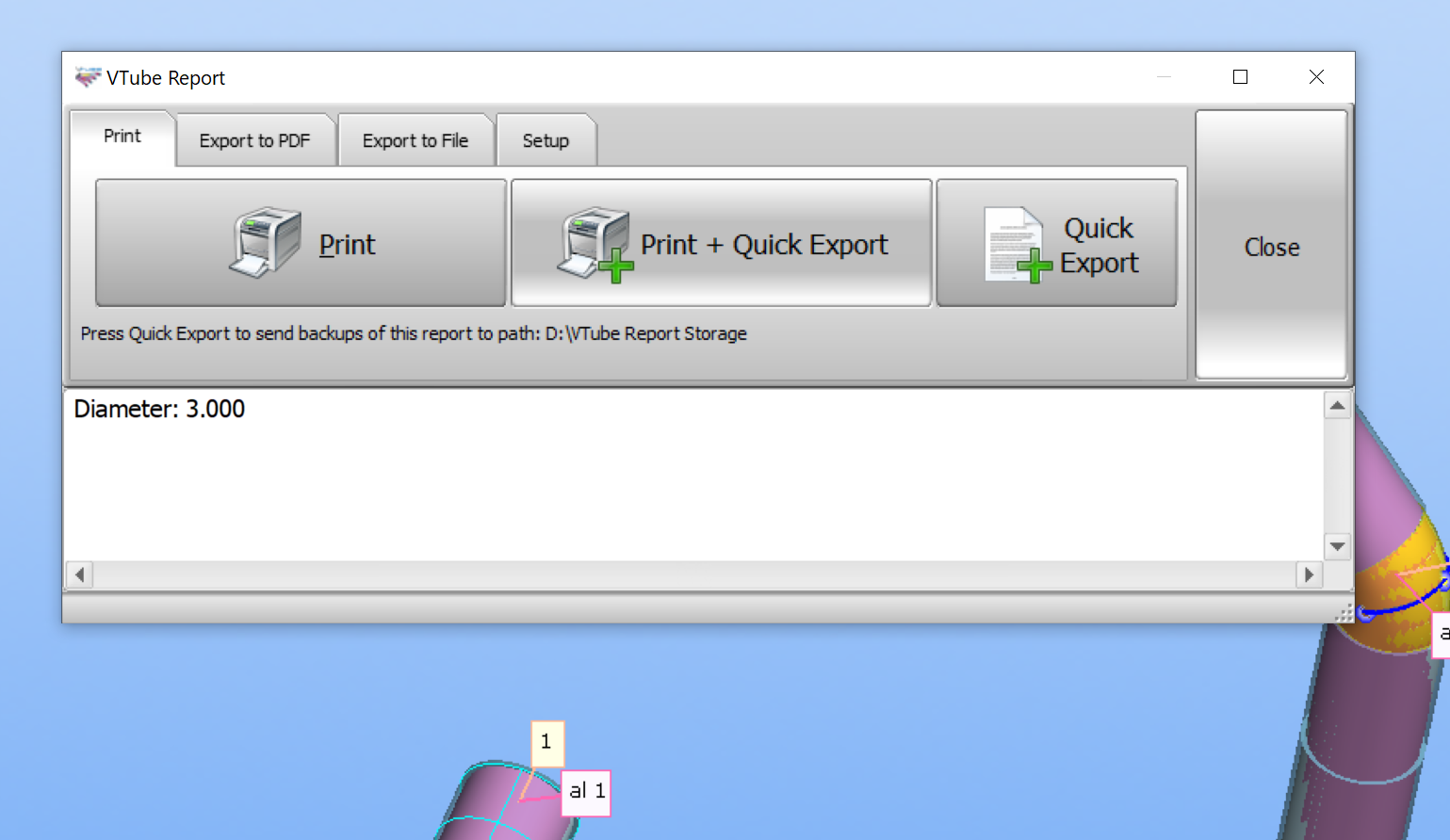
Here is an example CSV template (a report template file in VTube).
Diameter: <vtube_val>DIAMETER</vtube_val>
The report template builds a one-line report like this:
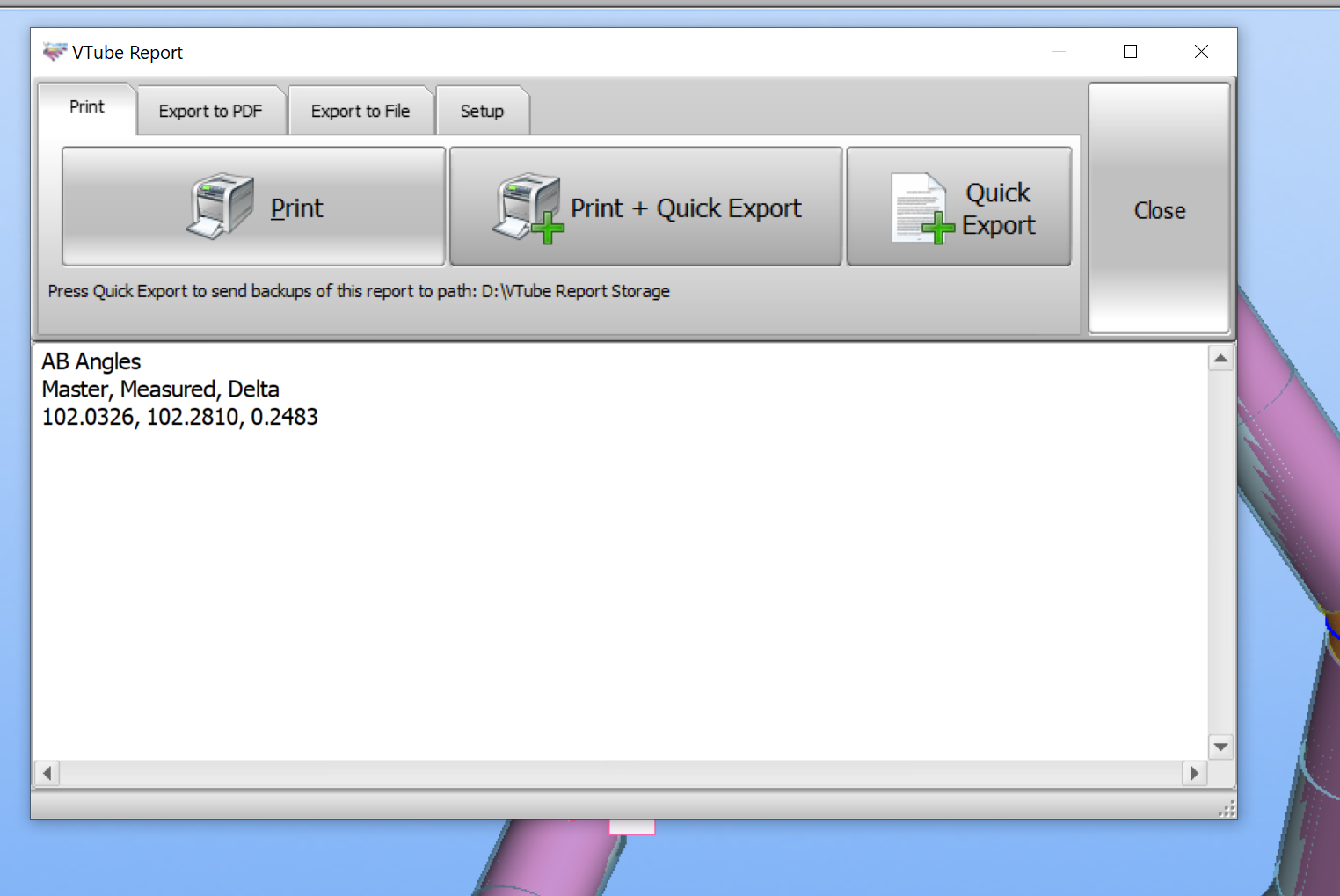
A slightly more complex report template example is:
AB Angles Master, Measured, Delta <vtube_val>AB-AngleMaster</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>AB-AngleMeasured</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>AB-AngleDelta1</vtube_val>
This report template creates a report like this:
About VTube's Token Tags
The only tags required in a CSV report template are the VTube's token tags <vtube_val>, </vtube_val>.
A "tag" is text that HTML uses to control formatting. Tags are enclosed in corner brackets < and >. So, <vtube_val> is a tag.
A "token" is a VTube term that means "a word that VTube replaces with a value." So, the tag <vtube_val> will be followed by token like DIAMETER. When VTube finds DIAMETER between the tags, it will replace it with an actual value, like "3.500." (Tokens are case-insensitive. DIAMETER, diameter, and Diameter are all the same to VTube.) See a List of Report Tokens.
If you have sections that iterate (like Bender data), then you will also need to use VTube's custom iterate tags: <vtube_iterate section=nnn>, and </<vtube_iterate>. See the Supravision CSV template below. Find the iterate sections.
To "iterate" means to repeat - like points or bender data repeats until all the data is in the report. See a List of HTML Iteration sections.
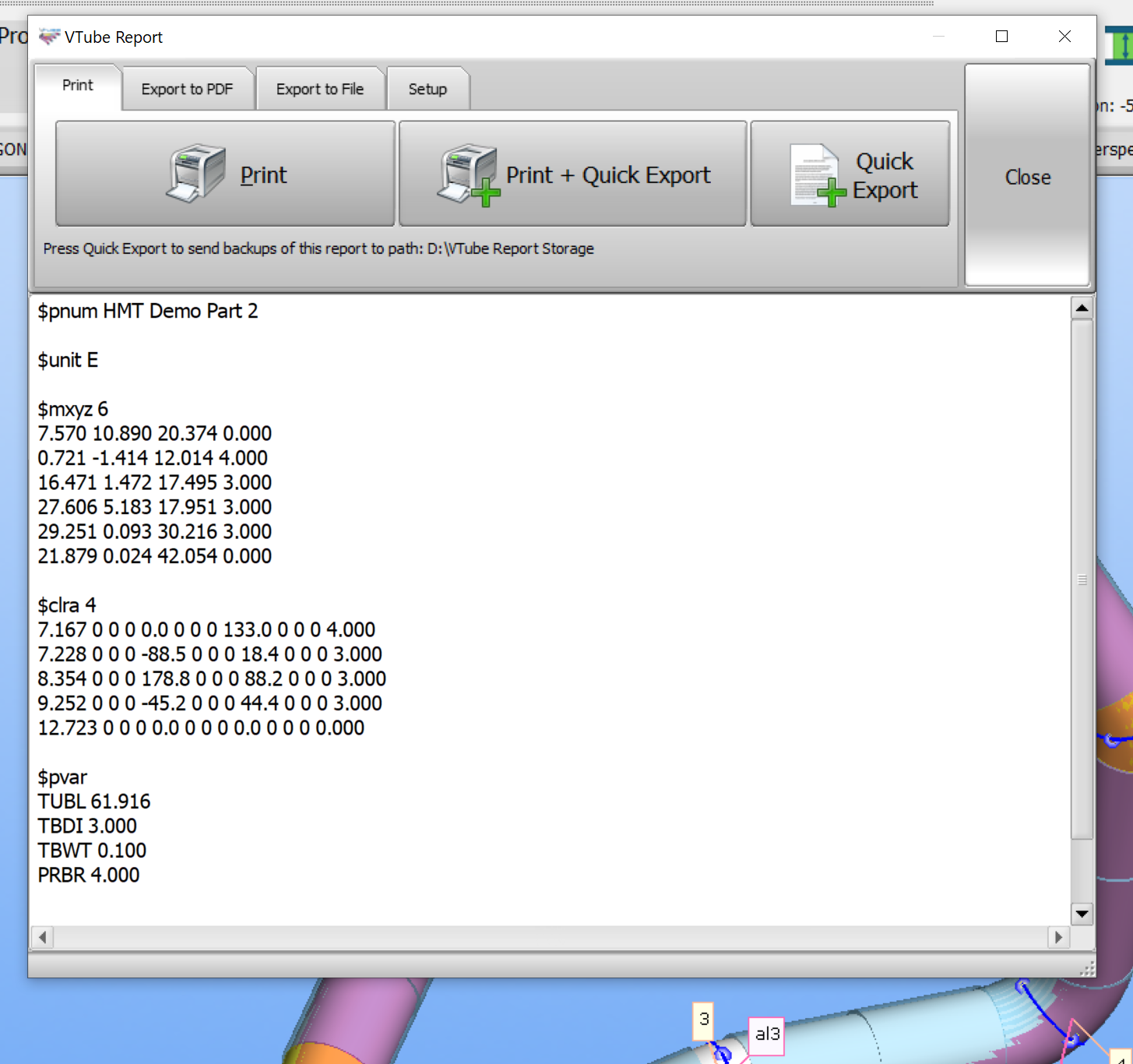
This CSV report template file creates a Supravision file output using both the token tags and the iteration tags.
$pnum <vtube_val>PARTNUMBER</vtube_val> $unit <vtube_val>LinearUnitSupravisionStyle</vtube_val> $mxyz <vtube_val>Points</vtube_val> <vtube_iterate section=XYZ> <vtube_val>Array_X</vtube_val> <vtube_val>Array_Y</vtube_val> <vtube_val>Array_Z</vtube_val> <vtube_val>Array_RADIUS_XYZ</vtube_val> </vtube_iterate> $clra <vtube_val>Bends</vtube_val> <vtube_iterate section=LRA> <vtube_val>Array_L</vtube_val> 0 0 0 <vtube_val>Array_R</vtube_val> 0 0 0 <vtube_val>Array_A</vtube_val> 0 0 0 <vtube_val>Array_RADIUS_LRA</vtube_val> </vtube_iterate> $pvar TUBL <vtube_val>cutlength</vtube_val> TBDI <vtube_val>diameter</vtube_val> TBWT <vtube_val>wall</vtube_val> PRBR <vtube_val>defaultradius</vtube_val>
This is the Supravision report built from the template above:
Delimiter Rules for the CSV Report Template
- Delimiters are the characters that separate values in a report. In English-language CSV reports, a comma is commonly used to separate values. However, like in the Supravision example above, other delimiters (like spaces) can also be used.
A "Delimiter" is a character that separates values in a report.
- If a locale is non-USA, it might use commas to separate the integer and fraction portion of a floating point number like "25,4". In this case, they could choose to use a semicolon as a separator like this:
25,4; 38,1; 1250,75
- Examples of other possible delimiter characters are /|\:`~!@#$%^&* () - and even the space character.
- Other than for the VTube variables and iterations, don't use the angle brackets (< or >) as delimiters because VTube removes HTML formatting tags in the output CSV file.
VTUBE REPORT MENUS - Choose HTML or CSV Report Formats - Use the Combo List in Report Menu
- The Report Menu shows a list of report templates. Each report template can be set to HTML or CSV format before you build a report.
- Use the combo list box for each report template to control which report format is built.
- In the Report Windows, HTML reports will display in the web-browser canvas to show complete formatting.
- CSV-formatted reports will display in a CSV text editor.
-
See this short introduction to VTube's new CSV format output capability for reports.
The CSV Viewer in the Report Window
- CSV reports will display in a text-viewer canvas that removes all the HTML formatting.
- From the viewer, you can output to a CSV, PDF, or Excel file.
- When CSV format mode is active, there is no Print Preview window.
- The CSV display is currently read-only. It will not allow for editing the text in the CSV report.
Example CSV Report Templates
Here are example CSV report templates you can download and import into VTube-STEP and VTube-LASER.
Report Template: CSV - Master XYZ + LRA Data.html
This template creates a CSV file for the Master XYZ and LRA data. It is appropriate for either VTube-STEP or VTube-LASER.
Copy this code to Notepad++, save it to "CSV - Master XYZ + LRA Data.html", then import it into VTube-STEP and VTube-LASER Report Menus.
Section: Setup Date: <vtube_val>DATE</vtube_val> Part Number: <vtube_val>PARTNUMBER</vtube_val> Customer: <vtube_val>customer</vtube_val> Fabricator: <vtube_val>organization</vtube_val> Technician: <vtube_val>author</vtube_val> Unit: <vtube_val>UNIT</vtube_val> Material Spec: <vtube_val>materialspec</vtube_val> Diameter: <vtube_val>DIAMETER</vtube_val> Wall: <vtube_val>wall</vtube_val> XYZ Points: <vtube_val>POINTS</vtube_val> Cut Length: <vtube_val>cutlength</vtube_val> Section: Master XYZ Centerline Column Definitions: Point, X, Y, Z, Radius <vtube_iterate section=XYZ> <vtube_val>Array_INDEX</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>Array_X</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>Array_Y</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>Array_Z</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>Array_RADIUS_XYZ</vtube_val> </vtube_iterate> Section: Master Bender Column Definitions: Num, Length, Rotation, Angle, Radius <vtube_iterate section=LRA> <vtube_val>Array_INDEX</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>Array_L</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>Array_R</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>Array_A</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>Array_RADIUS_LRA</vtube_val> </vtube_iterate>
Report Template: CSV - Tube Inspection Report.html
This template creates a CSV file for the Tube Inspection Report data. It is appropriate for VTube-LASER since VTube-LASER works with inspection data.
Copy this code to Notepad++, save it to "CSV - Tube Inspection Report.html", then import it into VTube-LASER Report Menu.
Section: Inspection Variables Part Number: <vtube_val>PARTNUMBER</vtube_val> Date/Time: <vtube_val>DATE</vtube_val> Unit: <vtube_val>UNIT</vtube_val> Comment 1: <vtube_val>COMMENT1</vtube_val> Overall Qualification: <vtube_val>PassFail_QualifierAttributes_Result</vtube_val> Qualification Attributes: <vtube_val>PassFail_QualifierAttributes_Setup</vtube_val> Qualification Tolerance Envelope: <vtube_val>defaulttolerance</vtube_val> A-End Length Qual Env Tolerance Positive: <vtube_val>A-EndLengthDifferenceTolerancePos</vtube_val> A-End Length Qual Env Tolerance Negative: <vtube_val>A-EndLengthDifferenceToleranceNeg</vtube_val> B-End Length Qual Env Tolerance Positive: <vtube_val>B-EndLengthDifferenceTolerancePos</vtube_val> B-End Length Qual Env Tolerance Negative: <vtube_val>B-EndLengthDifferenceToleranceNeg</vtube_val> A-End Angle Qual Env Tolerance: <vtube_val>A-EndAngleDifferenceTolerance</vtube_val> B-End Angle Qual Env Tolerance: <vtube_val>B-EndAngleDifferenceTolerance</vtube_val> Section: End-Length / End Angle Statistics Column Definitions: End, Length, Angle, End Offset Row Count: 2 A, <vtube_val>A-EndLengthDifference</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>A-EndAngleDifference</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>A-EndOffset</vtube_val> B, <vtube_val>B-EndLengthDifference</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>B-EndAngleDifference</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>B-EndOffset</vtube_val> Section: End-To-End Statistics Column Definitions: End-To-End Length, Tol Pos, Tol Neg, OOT <vtube_val>AB-LenDelta</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>AB-LenTolPos</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>AB-LenTolNeg</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>AB-LenOOT</vtube_val> Column Definitions: Master AB Angle, Measured AB Angle, AB Angle Delta <vtube_val>AB-AngleMaster</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>AB-AngleMeasured</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>AB-AngleDelta1</vtube_val> Section: Critical Point Statistics Row Count: <vtube_val>STRAIGHTS</vtube_val> Column Definitions: Straight, T1d, T1t, T1ot, MPd, MPt, MPot, T2d, T2t, T2ot, Avg, Max <vtube_iterate section=INSPECTION> <vtube_val>Array_INDEX</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>Array_DevT1</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>Array_TolT1</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>Array_T1_oot</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>Array_DevMP</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>Array_TolMP</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>Array_MP_oot</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>Array_DevT2</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>Array_TolT2</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>Array_T2_oot</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>array_dev_tmt_average</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>array_dev_tmt_maximum</vtube_val> </vtube_iterate> Section: Bender Data Deviations Row Count: <vtube_val>STRAIGHTS</vtube_val> Column Definitions: Num, Ldev, Rdev, Adev <vtube_iterate section=LRACOR> <vtube_val>Array_INDEX</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>Array_Lerr</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>Array_Rerr</vtube_val>, <vtube_val>Array_Aerr</vtube_val> </vtube_iterate>
CSV Report Automation
- Like PDF file automation, CSV files with unique names can be built automatically to a network location after a measure, then a measured-aligned event.
- The CSV Automation is in System Options > Report Automation tab menu on the far-right side of the screen.
- The Report Automation menu replaces the old PDF menu and has two new sub-menus: PDF Automation and CSV Automation.
- With this new structure, adding other new report build automation (like HTML automation, for example) will be possible. This approach allows ATT developers to add any report build automation that customers request that we have not yet imagined.